A research team led by Prof. Chen Wei from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has unveiled a groundbreaking invention-an all-weather hydrogen-chlorine (H2-Cl2) battery capable of withstanding extreme temperatures from a bone-chilling -70°C to a sweltering 40°C.
This study, highlighted as the cover article in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, represents a significant stride in pursuing efficient and versatile energy storage technologies.
(Photo: Image via J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023)
Making Hydrogen-Chlorine Batteries Rechargeable
Hydrogen fuel cells have long been hailed for their promise to deliver sustainable energy, primarily due to the abundance of hydrogen.
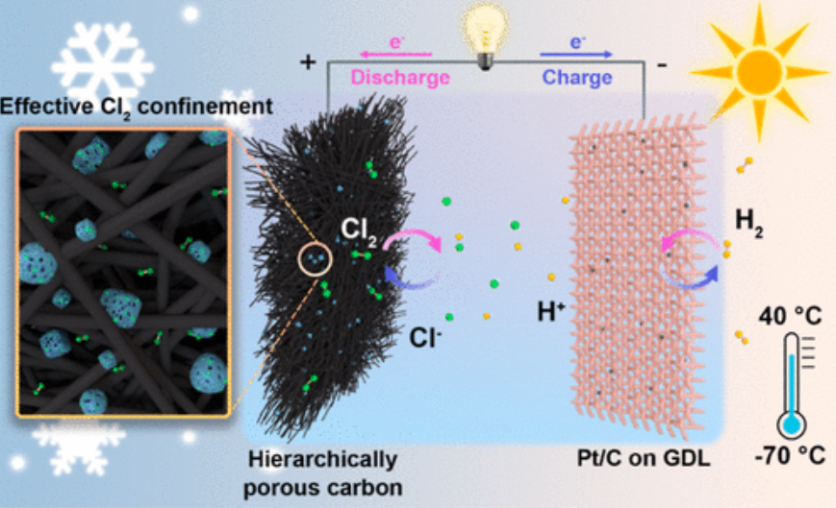
Among them, H2-Cl2 fuel cells stand out with their fast electrochemical kinetics, high redox potential, and robust, specific capacity of the Cl2/Cl- redox couple.
However, a persistent challenge has plagued these cells as the volatility of chlorine gas during the charging process, leads to poor Coulombic efficiency and reversibility.
This report shared by the Chinese Academy of Science tells us that the research team's journey began with the identification of a critical issue: traditional adsorptive cathodes struggled to immobilize Cl2 due to a lack of binding sites with a strong affinity for it, resulting in low reversibility.
The team ingeniously designed a hierarchically porous carbon cathode to overcome this hurdle, blending highly micro-/mesoporous carbon (HPC) and macroporous carbon felt (CF). This innovative approach effectively confined the elusive Cl2 on the cathode, unlocking enhanced reversibility.
Impressive Results, Unveiling the Mechanism
The H2-Cl2 cells showcased exceptional performance, maintaining high Coulombic efficiency and stability over an impressive 500 cycles at a discharge capacity of 3 mAh cm-2.
Their resilience in ultralow temperatures was even more noteworthy, boasting a discharge plateau of 1.1 V and a specific capacity of 282 mAh g-1 at a bone-chilling -70°C.
The research team turned to advanced techniques to unravel the mystery behind this improved reversibility. Combining X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with theoretical calculations illuminated the Cl2/Cl- reaction, revealing its correlation with the reversible formation and breakage of C-Cl bonds.
This groundbreaking insight into the battery's inner workings opens new avenues for designing aqueous chlorine batteries and high-energy-density hydrogen batteries across a broad temperature spectrum.
A New Frontier for Energy Storage
In simpler terms, the researchers have pioneered a rechargeable H2-Cl2 battery that not only overcomes the challenges posed by extreme temperatures but also offers a promising solution to the longstanding issues of Coulombic efficiency and reversibility.
This development represents a significant stride towards implementing hydrogen-chlorine batteries in real-world scenarios, transcending the limitations that have hindered their widespread adoption.
In Other News
A Florida court found "reasonable evidence" that Tesla CEO Elon Musk and other officials were aware of Autopilot system flaws but allowed hazardous cars to be driven.
Judge Reid Scott of the Circuit Court for Palm Beach County last week granted the plaintiff in a fatal collision case the right to sue Tesla for deliberate misconduct and gross negligence.
Stay posted here at Tech Times.
Related Article: University of Tokyo Unveils Cobalt-Free Lithium-Ion Battery Boosting Energy Storage by 60%

(Photo: Tech Times Writer John Lopez)




