Abstract: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become essential tools for organizations seeking to integrate and streamline business functions such as finance, human resources, sales, and manufacturing. However, ERP implementation remains a complex, multi-phase process characterized by both technical and organizational challenges. This study systematically reviews the critical success factors (CSFs) that influence successful ERP implementations, drawing insights from extensive literature and case studies. Key factors identified include effective change management, robust data management, strong management commitment, comprehensive project planning, proactive risk assessment, and strategic vendor partnerships. These elements play a pivotal role in addressing challenges such as resistance to change, system integration issues, and process reengineering complexities. By focusing on these CSFs, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, improve decision-making, and ensure a positive return on investment. This review provides valuable guidance for practitioners and scholars, offering a consolidated perspective on achieving successful ERP deployment in today's competitive business landscape.
Keywords: Enterprise Resource Planning, ERP implementation, critical success factors, change management, data management, management commitment, project planning, risk assessment, vendor partnerships, system integration, operational efficiency, digital transformation, organizational challenges, ERP systems, return on investment, business process reengineering, AI-driven ERP, ERP benefits, case studies, strategic implementation.
The topic of critical success factors for Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) implementation holds significant relevance in today's business landscape as organizations increasingly adopt these complex systems to enhance productivity and efficiency. ERP systems are integral for integrating various business functions, including financial management, human resources, sales, and manufacturing, thereby streamlining processes and improving data accuracy across the enterprise[1][2]. Implementing an ERP system, however, involves navigating a multi-phase process fraught with both technical and people-related challenges, underscoring the importance of identifying factors that can ensure successful deployment and operation[3][4].
A systematic literature review of ERP implementation provides a comprehensive examination of these critical success factors (CSFs), drawing insights from numerous academic articles and case studies. This extensive analysis identifies key elements such as change management, effective data management, strong management commitment, robust project planning, thorough risk assessment, and strategic vendor partnerships as pivotal to successful ERP implementation[5][6]. Each of these factors contributes uniquely to mitigating the inherent complexities of ERP projects, enhancing the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes and realizing the benefits associated with these systems[7].
Despite the potential advantages, the ERP implementation process is not without its challenges. Organizations often face resistance to change from employees, technical hurdles related to system integration, and the daunting task of reengineering existing business processes to align with the new system[8][9]. Furthermore, the substantial investment required for ERP systems, in terms of both financial resources and time, necessitates careful planning and execution to ensure a positive return on investment[10]. These challenges highlight the need for organizations to adopt a strategic approach, emphasizing continuous communication and risk management throughout the implementation lifecycle[11].
In summary, understanding the critical success factors for ERP implementation is essential for organizations seeking to maximize the benefits of their ERP systems. By focusing on these elements, companies can improve their operational efficiency, facilitate better decision-making, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries[12][13]. This systematic literature review serves as a valuable resource for practitioners and scholars alike, offering a consolidated view of the factors that drive successful ERP implementations and addressing the complexities involved in such transformative projects[14].
Background
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as vital strategic tools in today's competitive business environment, offering integration of various business functions such as financial management, human resources, sales, and manufacturing to enhance productivity and efficiency[1][2]. The implementation of ERP systems involves a complex, multi-phase process that includes planning, configuring, deploying the software, redesigning business processes, migrating data, and training users[2][3]. This complexity is compounded by the need to balance people-related challenges, such as resistance to change, with technical obstacles[4].
Successful ERP implementation is often characterized by the identification of critical success factors, critical people, and critical uncertainties that can influence the outcome of the project[1]. These elements are vital in future-proofing ERP systems to ensure they continue to work seamlessly with new technologies despite the significant costs associated with updates and potential reimplementation[5]. Additionally, challenges such as the daunting array of features within an ERP system can be mitigated through thorough training and the provision of access to only the necessary modules for each job role[6].
In response to these challenges, organizations are encouraged to maintain clear communication channels, establish contingency plans, and regularly update risk registers to manage unforeseen risks effectively[7]. This systematic approach can help mitigate the drawbacks while maximizing the benefits of ERP systems, ensuring that the significant investment in such systems yields a positive return on investment[5]2].
Methodology
The methodology for this study on critical success factors (CSFs) in enterprise resource planning (ERP) system implementation involved a systematic review approach. This approach was chosen to provide a comprehensive overview of the existing literature and identify key factors that influence the successful implementation of ERP systems in organizations[8][9].
Initially, a systematic review of relevant articles was conducted, targeting five different databases as well as several international conference proceedings[8][10]. This involved applying specific search terms such as "ERP," "Enterprise Resource Planning," and "ERP success factors" to gather relevant articles. The search was intentionally limited to publications from 2000 to 2013 to ensure the inclusion of relatively recent and pertinent studies[9][1].
The literature review process was structured around the five steps proposed by Khan et al. (2003) for conducting systematic reviews, which included selecting articles, reviewing their content, and conducting quality assessments[9]. This rigorous process resulted in the identification of 320 relevant papers, comprising 144 single or multiple case studies, 118 surveys, and 58 literature reviews or articles from which CSFs could be derived[10]. The selected articles were further categorized based on their primary focus, facilitating a detailed analysis of the critical factors highlighted in these studies[1].
Through this methodology, the research aimed to fill existing gaps by providing a consolidated view of the literature on CSFs for ERP implementation while also considering the perspectives of different participants in the field[9].
Critical Success Factors
Critical Success Factors (CSFs) play a vital role in ensuring the success of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) implementations. Identifying and understanding these factors can significantly improve the chances of achieving desired outcomes and realizing the benefits of an ERP system[8][10]. The following are key CSFs that have been empirically validated through systematic literature reviews and practical implementations.
Change Management
Change management addresses the human aspect of ERP implementations, mitigating resistance to change by engaging stakeholders across all levels of the organization[11][12]. Cultivating leaders within the organization to champion the project and providing thorough communication and training can help ease the transition and improve user acceptance[13][14].
Data Management
Effective data management, including data migration and hygiene, is crucial for ERP implementation. Consolidating and transferring data to a central database ensures accuracy and helps eliminate redundant information, thus maintaining project timelines and budgets[15]. Properly managing data migration can prevent issues such as duplicate or inaccurate data, which can cause go-live delays[15].
Management Commitment
Senior management involvement is crucial for the successful implementation of ERP systems. Their commitment ensures that the necessary resources are allocated and strategic decisions are made promptly[4][13]. Effective leadership can maintain high morale and guide the project through challenges, ensuring alignment with the organization's unique business objectives[16][17].
Project Planning and Governance
A comprehensive project plan acts as a roadmap, guiding all stakeholders towards clear objectives and expectations[18]. Phased implementation with clear milestones can help manage complexities and maintain control over project direction, scope, and structure[2]. Effective project governance is essential for coordination, timely execution, and resource allocation[18].
Risk Assessment and Management
Conducting a thorough risk assessment ensures that potential challenges are identified and mitigated proactively. Aligning the implementation strategy with ongoing organizational strategies helps in navigating uncertainties and reducing implementation risks[16][18].
Vendor Selection and Partnership
Choosing the right vendor is critical for ERP success. It involves conducting deep research, defining clear selection criteria, and involving key stakeholders in the evaluation process[5].
Establishing a strong partnership with the vendor through effective negotiation and contract management ensures alignment with business needs and a successful implementation[5][6].
By focusing on these critical success factors, organizations can enhance their ERP implementation efforts, achieving streamlined operations, enhanced productivity, and improved decision-making capabilities[17][3].
Benefits of Successful ERP Implementation
The successful implementation of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance organizational performance. One of the primary advantages is increased productivity and efficiency. By integrating various business functions such as financial management, human resources, sales, and manufacturing into a unified system, ERP allows for streamlined processes and more efficient workflows[2]. This integration provides a single, accurate source of data, which is essential for informed decision-making across the organization[15][3].
Another significant benefit of ERP implementation is the facilitation of data migration. This involves consolidating data from multiple systems into a central database, thus ensuring data consistency and availability across the organization[15][3]. Additionally, ERP systems help in aligning business processes with organizational goals, which can lead to improved performance and competitive advantage[2].
Successful ERP implementation also contributes to better resource management. By providing visibility into various business processes, ERP systems enable organizations to manage resources more effectively, reducing waste and improving the allocation of resources[2]]. Moreover, the data integration provided by ERP systems enhances the organization's ability to adapt to changes in the business environment, providing a strategic advantage[3].
Finally, the implementation of an ERP system can lead to long-term financial benefits. Despite the initial costs of purchasing, customizing, and maintaining the system, as well as training employees, enhanced productivity and efficiency can lead to substantial cost savings over time[6][17]. For example, tools can be used to estimate savings after one and three years, helping organizations determine when returns will surpass costs[6]. In summary, the successful implementation of an ERP system not only streamlines operations and enhances productivity but also drives organizational growth and improves decision-making capabilities[17].
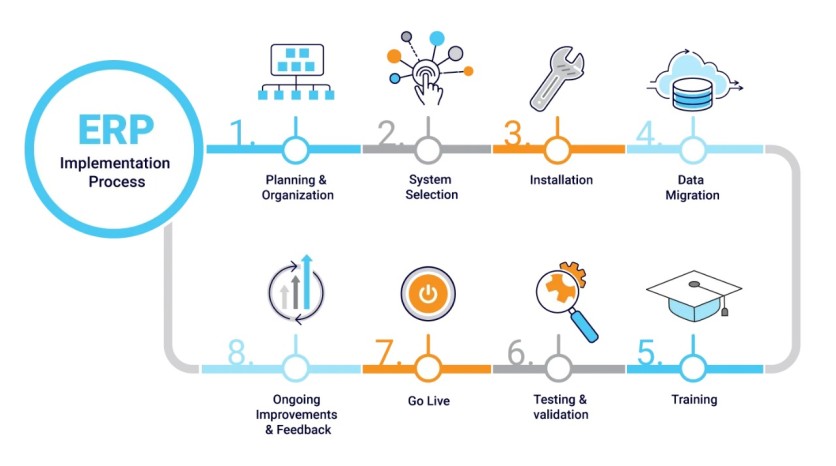
Challenges in ERP Implementation
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system presents numerous challenges that organizations must navigate to achieve a successful deployment. One of the primary challenges is balancing the integration of technology with the management of people within the organization. Employees often exhibit resistance to change, a common people-related obstacle, as they adjust to new processes and systems[4].
Additionally, the technical complexities involved in ERP implementation can pose significant hurdles. The ERP system integrates various business functions, such as financial management, human resources, sales, and manufacturing, aiming to enhance productivity and efficiency[2]. However, the multifaceted nature of ERP systems makes the implementation process inherently complex. This complexity arises from the need to carefully plan, configure, and deploy the system while ensuring that it aligns with the organization's requirements and enhances existing business processes[2].
Moreover, ERP implementation is a multi-phase project that can extend over several months, and in large organizations, it may last up to a year. This duration adds to the challenge, as it requires sustained commitment and coordination across different departments[3]. The process involves redesigning business processes to leverage the new system's capabilities, configuring the software, migrating data, and conducting extensive user training[3]. Rigorous testing before full deployment is crucial to address any technical issues that could disrupt operations[2].
Case Studies
Case studies play a pivotal role in understanding the critical success factors (CSFs) for enterprise resource planning (ERP) system implementations. Through an extensive review of the literature, numerous case studies have been analyzed to extract valuable insights into the success and failure of ERP projects. Among the 320 relevant papers identified in a comprehensive systematic review, 144 were single or multiple case studies specifically focused on ERP implementations[10].
These case studies provide in-depth analyses of various real-world scenarios where organizations attempted to implement ERP systems. The findings from these studies reveal that successful ERP implementations often hinge on careful planning, a clear definition of organizational requirements, and effective process redesign to leverage the capabilities of the new system[2]. Moreover, rigorous testing and user training are emphasized as essential steps in ensuring that the ERP system is well-integrated and utilized effectively by the end-users[3].
Challenges identified through case studies include determining which existing processes would benefit from ERP integration and managing the complexities associated with different divisions within an organization[19]. These challenges underline the importance of having a comprehensive understanding of the organization's processes and clear communication among stakeholders throughout the ERP implementation project.
References
[1] Al-Fawaz, K., Al-Salti, Z., & Eldabi, T. (2008). Critical success factors in ERP implementation: A review. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/49401950_Critical_success_factors_in_ERP_implementation_A_review
[2] Schwarz, L. (2024, February 19). 6 Key Phases of an ERP Implementation Plan. NetSuite. https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/erp/erp-implementation-phases.shtml
[3] Caldwell, A. (2020, October 2). 7 Key ERP Implementation Challenges and Risks. NetSuite. https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/erp/erp-implementation-challenges.shtml
[4] Invoicera. (n.d.). Top 10 Challenges in ERP Implementation. Invoicera. https://www.invoicera.com/blog/business-operations/common-challenges-in-erp-implementation/
[5] Forbes Technology Council. (2024, May 3). ERP Implementation: 17 Common Challenges (And How To Overcome Them). Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2024/05/03/erp-implementation-17-common-challenges-and-how-to-overcome-them/
[6] McCue, I. (2024, November 22). What is ERP? A Comprehensive Guide. NetSuite. https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/erp/what-is-erp.shtml
[7] Pharos Solutions. (2024, March 29). ERP Project Management: Best Practices and Implementation Guide. Pharos Solutions. https://www.pharossolutions.com/pharos-solutions-blog/erp-project-management-best-practices-and-implementation-guide
[8] Mahraz, M.-I., Berrado, A., & Benabbou, L. (2019, March). Success Factors for ERP Implementation: a Systematic Literature Review. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355864958_Success_Factors_for_ERP_Implementation_a_Systematic_Literature_Review
[9] Tarhini, A., Ammar, H., Tarhini, T., & Masa'deh, R. (2015, March). Analysis of the Critical Success Factors for Enterprise Resource Planning Implementation from Stakeholders' Perspective: A Systematic Review. International Business Research, 8(4), 25-40. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273575189_Analysis_of_the_Critical_Success_Factors_for_Enterprise_Resource_Planning_Implementation_from_Stakeholders'_Perspective_A_Systematic_Review
[10] Leyh, C., & Sander, P. (2015). Critical Success Factors for ERP System Implementation Projects: An Update of Literature Reviews. In D. Sedera, N. Gronau, & M. Sumner (Eds.), Enterprise systems: Strategic, organizational, and technological dimensions (Vol. 198, pp. 33–45). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17587-4_3
[11] Baker, P. (2024, February 6). Top change management tips for ERP implementation success. TechTarget. https://www.techtarget.com/searcherp/feature/Top-change-management-tips-for-ERP-implementation-success
[12] Ultra Consultants. (2024, March 29). Smart Implementation: 6 Critical Change Management Strategies. Ultra Consultants. https://ultraconsultants.com/erp-software-blog/smart-implementation-6-critical-change-management-strategies/
[13] Hoffman, S. (2024, August 19). ERP Implementation Plan: 7 Key Phases. Software Connect. https://softwareconnect.com/learn/change-management-strategies-erp-implementation/
[14] Dynamics Insights. (2020, October 7). Effective Change Management is the Key to a Successful ERP Implementation. ArcherPoint. https://archerpoint.com/effective-change-management-key-successful-erp-implementation/
[15] Process Master Technologies Pvt Ltd. (2022, July 21). 6 Common ERP Implementation Challenges faced by SMEs. Probiz ERP. https://probizerp.com/blog/6-common-erp-implementation-challenges-faced-by-smes/
[16] Indeed Editorial Team. (n.d.). 11 Critical Success Factors for ERP Implementation (With Definition). Indeed. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/critical-success-factors-for-erp-implementation
[17] | Inbound Logistics. (2023, August). Enterprise Resource Planning: Definition, Benefits, and Challenges. Inbound Logistics. https://www.inboundlogistics.com/articles/enterprise-resource-planning/
[18] Biswas, N. (2024, June 11). How to Mitigate Implementation Risks with ERP Project Management? Focus Softnet. https://www.focussoftnet.com/blogs/mitigating-implementation-risks-for-ERP-project-management
[19] YourShortlist. (n.d.). 6 Common Challenges of ERP Implementation. YourShortlist. https://yourshortlist.com/6-common-erp-challenges/
About the Author

Sagar Gupta is a seasoned technology leader with over 20 years of experience specializing in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) implementations, digital transformation, and emerging technologies. As ERP Implementation Leader, Sagar has successfully directed numerous ERP projects, leveraging systems like NetSuite and Microsoft Dynamics to drive operational efficiency and organizational growth. His expertise spans cloud infrastructure, AI integration, and agile methodologies, enabling businesses to navigate complex technology landscapes. Sagar is passionate about delivering transformative solutions that align technology with strategic business goals, and his work reflects a commitment to innovation, collaboration, and measurable outcomes.




