Artificial Intelligence has changed industries and our daily lives by making things smarter and more efficient. However, traditional AI models are built on centralised systems where data is collected, processed, and stored in big centralized servers. This centralization raises questions about data privacy, security, and monopolistic control.
Enter decentralized AI—a new way of distributing AI across multiple nodes or devices, making it more secure, fair, and transparent.
So, what does DeAI mean for you? The short version is: For everyday tech users, decentralized AI means AI applications will be more accessible and trustworthy and will put you in control of your data.
Here's a deeper look.
Decentralized AI Explained: No More Central Servers
Decentralized AI gets rid of the single central server by spreading data processing across a network of nodes. These nodes can be individual devices or servers working together to analyze and process data.
This is often built on blockchain, which provides a transparent and tamper-proof record of all transactions and computations.
This is in contrast to centralized AI systems. Traditional AI is done through centralized hubs run by big corporations like Google, Amazon, or OpenAI. While efficient, these systems require users to send their data to remote servers, which raises privacy and security concerns.
Centralized systems also risk creating monopolies where control of AI is concentrated in a few hands, which can lead to biases and inequalities in how AI is developed and deployed.
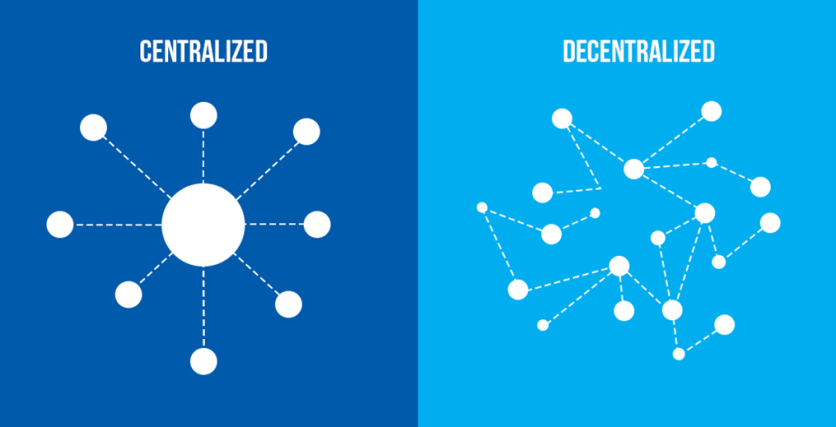
Decentralized AI mitigates these risks. It decentralizes both the processing power and the decision-making process, making it more collaborative and transparent. Users control their data, and the AI operates more democratically.
We asked Dr. Max Li, founder and CEO of OORT, cloud solutions for decentralized AI applications, to explain the limitations of centralized AI systems and the transformative potential of decentralized AI.
"Centralized AI systems are controlled by big companies and rely on massive central servers," he explained. "That creates significant issues, like privacy risks and especially biased outcomes."
He continued, "Decentralized AI addresses these problems by spreading the work across a network of devices rather than relying on a single server. It also diversifies data collection by involving people from varied backgrounds."
"It's not just about better technology—it's about making AI more open, fair, and accessible for everyone."
Dr. Li continued to mention the key pillars of the AI industry and the potential for decentralization to disrupt centralized control.
"There are three pillars in the AI industry—compute, data, and models," he tells Tech Times. "The big players dominate AI because of their computing power and advanced models."
He emphasized that decentralizing data collection, storage, and computing power can make AI more scalable and break the bottleneck created by conglomerates.
"It's undoubtedly the direction our technology will evolve toward," Dr. Li concluded.
How Decentralized AI Protects Privacy and Security
One of the biggest benefits of decentralized AI is that it protects privacy and security. In traditional AI systems, user data is sent to centralized servers for processing. This is risky as centralized systems are the target of hackers. High-profile breaches of centralized databases have exposed the personal data of millions and eroded trust in such systems.
Decentralized AI solves this by keeping data on the user's device. For example, instead of sending health data to a central server, decentralized AI can process that data on a smartphone or wearable device. The blockchain technology used in decentralized AI systems also adds an extra layer of security by providing an immutable record of all data transactions. This means data can't be tampered with or accessed without proper authorization, reducing the risk of breaches.
This model respects user privacy in addition to security. Sensitive information no longer needs to be shared with third parties as computations happen locally. This matches the growing demand for privacy-preserving technologies, especially in regions with strict data protection laws like the European Union's GDPR.
Making AI More Accessible to Everyone
Decentralized AI makes AI accessible to everyone. Centralized AI systems require a lot of money and technical resources to run and are out of reach for smaller organizations and individuals. Decentralized AI distributes the computational load across many nodes, so any single node doesn't require a lot of infrastructure.
This allows even individuals with limited resources to participate in AI or benefit from AI tools. For example, decentralized AI-powered platforms like SingularityNET allow developers to contribute AI models to a shared marketplace. These models can then be accessed and used by anyone to foster global innovation and collaboration.
For end users this means more affordable and more AI applications. Small businesses can use AI tools without the high costs of centralized systems. Developers from underrepresented regions can contribute to and benefit from decentralized AI networks to increase innovation.
Building Trust Through Transparency
Trust has been a big issue with AI. Centralized systems are often opaque, with no information on how AI models make decisions or process data. This lack of transparency can lead to biases, unfair outcomes, and user distrust.
Decentralized AI is transparent by design. Many decentralized AI systems are open-source, and their code and decision-making process is public. Blockchain technology provides an immutable record of all AI computations so every decision or transaction can be traced and verified.
This transparency not only builds trust but also reduces biases. Decentralized AI systems can ingest diverse data sources and perspectives so the outcomes are more balanced and fair. For example, an AI model trained on decentralized global datasets will not reflect the biases of a single organization or region.
Decentralized AI Use Cases
Decentralized AI isn't just a theory; it's already happening. From healthcare to smart home devices, the possibilities are endless.
Healthcare
In healthcare, decentralized AI can change how patient data is managed and used. Traditional healthcare systems require patients to share sensitive data with centralized databases and risk breaches and misuse. Decentralized AI allows patients to keep control of their data and get advanced analysis.
For example, a decentralized AI model could analyze health data from wearables on the user's device. This local analysis gives personalized health insights without compromising privacy. Decentralized AI also enables secure data sharing between healthcare providers, allowing collaboration without patient confidentiality risk.
Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices like virtual assistants and IoT sensors rely on AI for functionality. However, these devices send user data to centralised servers for processing, which raises privacy concerns. Decentralized AI solves this by processing data on the device.
This local processing improves privacy and performance. Devices can respond faster to user commands without an internet connection. Decentralized AI lets users customize their smart home systems without being locked into a specific ecosystem controlled by one company.
Financial Services
In finance, decentralized AI is changing how transactions are done and secured. By combining AI with blockchain, decentralized financial platforms can offer smarter, more personalized services while keeping it secure.
For example, decentralized AI can analyze spending patterns to offer financial advice or detect real-time fraudulent transactions. Since this happens on a decentralized network, users are less exposed to centralized breaches. This is also in line with DeFi principles to remove intermediaries and give more access to financial services.
Challenges Decentralized AI Still Faces
It's not all good news. One of the biggest challenges is the infrastructure to support distributed systems. Decentralized AI needs a network of nodes that can process big data, which is resource-hungry.
Standardization is another problem. With multiple organizations building their own decentralized AI frameworks, interoperability between systems is an issue. We need to create common standards so different platforms can talk to each other.
And ethics. While decentralized AI is transparent, we still need to ensure its responsible use. Developers must consider misuse, such as biased or harmful AI models, and implement safeguards to prevent it.
Dr. Li broke down the main challenges facing decentralized AI and the importance of diversified data sources for fair and unbiased outcomes.
"The biggest challenge right now is building the infrastructure to handle all the data and computations across a network—it's not easy to manage," he explained. "Another issue is the lack of clear standards. For example, if all the data used to train an AI model comes from North America, how can we trust the AI to accurately understand and serve Asians?"
He noted that the nuances of daily life when amplified by AI, underscore the need for diverse data sources.
"It's already well-recognized in the industry that fair and unbiased AI comes from diversified, open-source, and publicly collected data," Dr. Li concluded.
Looking Forward
Decentralized AI is a game changer for how AI is developed and used. By distributing the processing power and decision-making, this solves many of the problems with traditional AI systems, data privacy, accessibility, and trust.
For regular tech users, decentralized AI means smarter, more secure apps that respect their privacy and give them equal access to the latest tech. While there are challenges, the benefits make decentralized AI a winner for the future of AI. As this develops, it will be a big part of the digital landscape.
ⓒ 2026 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.






