Abstract: Dynamic automation is transforming the healthcare industry by enhancing efficiency, productivity, and patient care outcomes. This approach leverages flexible, reusable code modules to streamline complex workflows such as claim processing, patient enrollment, prescription management, and electronic health record (EHR) systems. Dynamic automation addresses the challenges of rapidly changing regulatory and operational requirements by enabling faster development and testing, reducing efforts by approximately 40%. While automation offers significant benefits—improved scalability, adaptability, and patient safety—its implementation faces challenges, including constant system updates and substantial initial investment. Agile frameworks play a crucial role in overcoming these barriers by fostering iterative development and collaboration across teams. Overall, dynamic automation has the potential to revolutionize healthcare services, leading to better health outcomes and improved operational efficiency.
Keywords: Dynamic Automation, Healthcare Automation, Prescription Processing, Claim Processing, Electronic Health Records (EHR), Agile Frameworks in Healthcare, Process Improvement, Healthcare Efficiency, Patient Care Automation, Automation in Pharmaceuticals, Health Data Management, Workflow Automation, Reusable Code Modules, Healthcare Technology, Patient Enrollment Automation.
Dynamic automation in the healthcare industry is a rapidly evolving field that leverages advanced technologies to streamline various processes and enhance patient care. This approach involves the use of automated systems to handle repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as claim processing, patient enrollment, prescription processing, drug utilization reviews, and more. By incorporating automation, healthcare providers can improve the quality of deliverables, ensure better accessibility to critical patient and prescription data, and open doors to innovative solutions that benefit patients, prescribers, and healthcare service companies[1][2][3].
One of the key innovations in this field is the concept of dynamic automation, which customizes the execution of code components through configurations via solution modeling. This method divides the execution process flow into multiple functional reusable capabilities, allowing for easier maintenance and testing. Dynamic automation addresses the challenges of frequently changing requirements and timeline constraints that often plague static automation workflows. For instance, in the complex process of prescription fulfillment, dynamic automation ensures that updates are seamlessly integrated without significant disruptions, thereby providing a robust and flexible solution[2][3].
Despite its numerous benefits, the implementation of dynamic automation in healthcare is not without challenges. Building automation involves significant investment and is time-consuming, often requiring extensive requirement gathering, design, development, and testing phases. Furthermore, the frequently changing requirements necessitate constant updates and retesting of code components, making the implementation process difficult and labor-intensive. To address these issues, healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting process improvement management frameworks like Agile, which emphasize iterative development and collaboration among cross-functional teams[4][5].
The potential advantages of dynamic automation are substantial. It can save approximately 40% of development and testing efforts, reduce the time to market, and facilitate multi-threaded automation execution, enhancing overall efficiency and productivity. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, dynamic automation stands out as a promising approach to meet the growing demands for better health outcomes and improved operational efficiency. This dynamic and adaptable method not only streamlines workflows but also ensures that healthcare providers can deliver timely and effective care, ultimately leading to better patient satisfaction and health outcomes[6][7].
Applications of Automation in Healthcare
Automation in the healthcare industry has found extensive applications in various domains, significantly enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and patient care. These automated systems streamline processes and reduce the burden on healthcare professionals by taking over repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
Claim Processing
One of the primary applications of automation in healthcare is in claim processing. Automated systems help in the swift and accurate processing of insurance claims, reducing errors and speeding up the reimbursement process. This is crucial for maintaining the financial health of healthcare institutions and ensuring that patients receive timely care.
Patient Enrollment and Management
Automation facilitates patient enrollment by streamlining data entry and verification processes. It ensures that patient information is accurately recorded and easily accessible to healthcare providers, enhancing the overall patient management process. Automated systems can also manage patient scheduling, reminders, and follow-ups, reducing no-show rates and improving patient compliance with treatment plans[1][2].
Prescription Processing and Drug Utilization Review
Automation plays a critical role in prescription processing by ensuring that prescriptions are accurately filled and that there are no harmful drug interactions. Automated systems can validate drug interactions, check for prior authorizations, and enforce days supply rules, thereby enhancing patient safety and compliance[3]. These systems also enable healthcare providers to monitor and review drug utilization patterns, contributing to better medication management.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management
The adoption of Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems has been widespread, with a significant percentage of hospitals and office-based physicians implementing these systems. Automation in EHR management improves the accessibility and accuracy of patient data, which is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment[3][4]. Automated EHR systems facilitate seamless data retrieval and sharing across different healthcare settings, ensuring continuity of care.
Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
Automated appointment scheduling systems help reduce the incidence of missed appointments by sending reminders to patients via email, text, or voice notifications. These systems can also manage appointment rescheduling and cancellations, optimizing the use of healthcare resources[2]. Tools like Cliniconex and Appointment Reminder have been particularly effective in reducing no-show rates and improving patient adherence to their healthcare plans.
Billing and Coding
Automation streamlines the billing and coding process, reducing the administrative burden on healthcare staff and minimizing errors. Automated systems ensure that billing codes are accurately assigned based on the services provided, which is essential for proper reimbursement and financial management within healthcare institutions.
Remote Patient Monitoring and Follow-Up
Automation enables remote patient monitoring through the use of sensors, wearable devices, and mobile applications. These systems allow healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs and health metrics in real time, facilitating early detection of potential health issues and timely interventions. Automated reminders for follow-up appointments and medication adherence further enhance patient outcomes[1][5].
Laboratory and Diagnostic Services
In laboratory and diagnostic services, automation helps in the accurate and efficient processing of tests and analyses. Automated systems can handle large volumes of samples, perform repetitive tasks, and deliver precise results, thereby improving the overall quality and speed of diagnostic services.
Benefits of Automation in Healthcare
Automation in healthcare offers numerous advantages, significantly transforming various aspects of patient care, operational efficiency, and overall healthcare delivery.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Automation has been successfully implemented in numerous industries to enhance quality, productivity, efficiency, timeliness, and operational safety while also reducing costs and delivering better value to customers. This same potential exists within the healthcare sector, where automation can streamline routine and repetitive tasks such as claim processing, patient enrollment, prescription processing, and drug utilization reviews[6]. By automating these processes, healthcare organizations can increase the quality of deliverables and accessibility to critical patient and prescription data[1].
Enhanced Patient Care
One of the significant benefits of automation in healthcare is the enhancement of patient care. Automation can ensure patient information is always available when needed, simplifying various care processes such as patient indexing, data entry, and accessing medical history. This continuous availability of data helps healthcare providers closely monitor patients, remind them of follow-up appointments, and facilitate faster billing processes, thereby improving overall patient satisfaction and care outcomes[1].
Data Quality and Accessibility
Access to high-quality data is crucial when seeking to automate healthcare workflows. The data used to support automation includes administrative, cost, frequency, duration, clinical, and outcome data. Automation ensures that these data points are reliable, accurate, and consistently available, which is critical for identifying automation opportunities and developing effective solutions[7]. The use of industry consensus standards further improves the quality of data, making it suitable for various automation needs[7].
Reduction in Missed Appointments
Automation can significantly reduce the number of missed patient appointments by integrating appointment reminders. This enhancement in communication between patients and healthcare providers ensures better adherence to scheduled appointments, thereby improving overall care continuity and patient outcomes[1].
Scalability and Adaptability
Dynamic automation, a process where the execution of code components is customized through configurations via solution modeling, offers considerable scalability and adaptability benefits. Since the automation code is broken into small, reusable components, it can be easily maintained, tested, and updated as needed. This flexibility ensures that any new changes or updates are dynamically accounted for during the execution process, reducing redundant development and maintenance work[6].
Long-term Benefits of AI Integration
In the longer term, automation combined with artificial intelligence (AI) can augment the care provided by healthcare professionals. AI can help clinicians examine "digital twin" models of patients, allowing them to test the effectiveness, safety, and experience of interventions in a digital environment before actual implementation. This innovative approach can lead to safer, standardized, and more effective patient care at scale[5].
Reduced Development and Testing Effort
Dynamic automation can save approximately 40% of development and testing effort, thus reducing the time to market for new automation solutions. This increased efficiency enables healthcare providers to implement automation solutions faster, thereby enhancing service delivery and patient care[6].
Challenges in Implementing Automation
Implementing automation in the healthcare industry presents a unique set of challenges that must be carefully navigated to ensure successful outcomes. One of the foremost hurdles is securing buy-in and trust among relevant stakeholders, such as patients, caregivers, clinicians, and staff, who are directly affected by the change. Without their investment, the adoption and effective use of automation solutions may be compromised[7].
Automation in healthcare also involves significant investments in time and resources for tasks such as requirement gathering, design, development, and testing[6]. Unlike other industries where automation has improved efficiency, quality, and safety, healthcare faces additional complexities. For example, electronic health records (EHRs) and clinical decision support systems (CDSS) depend on data from dynamic external systems, which can introduce novel deficiencies and increase the cognitive workload for healthcare professionals during the initial implementation phase[4][8].
Frequent changes in requirements and the need for continuous updates add another layer of complexity to healthcare automation projects[6]. These updates often necessitate retesting and modifying several code components, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Consequently, automation developers may find themselves reworking the same code and functionalities multiple times, further complicating the implementation process[6].
Moreover, the current state of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare is not yet advanced enough to reason like human physicians, relying instead on pattern recognition from datasets. This limitation underscores the need for continuous oversight and updates to ensure the AI systems remain effective[5].
Finally, the dependency on electronic systems raises concerns about operational continuity in the event of system failures, such as power outages. A robust recovery plan is essential to maintain healthcare services despite potential disruptions in electronic records. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive and dynamic approach to automation tailored to the specific needs and intricacies of the healthcare industry[9].
Process Improvement Management Frameworks
Implementing dynamic automation in the healthcare industry often requires leveraging robust process improvement management frameworks to address the complexities and evolving nature of healthcare workflows. One of the most widely adopted frameworks in this context is Agile, which has proven to be instrumental in reducing the time required to develop and deploy automation solutions[10].
Agile emphasizes iterative development, where requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between cross-functional teams. This framework is particularly beneficial in the healthcare sector due to the frequently changing requirements and regulatory constraints that necessitate constant updates and retesting of automation code[6]. By breaking down the automation development lifecycle into manageable sprints, Agile enables faster delivery of functional components, thereby accelerating the overall automation deployment process[10].
Another critical aspect of process improvement in healthcare automation is the need for a comprehensive technical infrastructure that can support dynamic and scalable automation activities. This involves building on established automation goals and desired outcomes and continuously monitoring and improving the system to ensure it meets the evolving needs of stakeholders[7]. The framework should also facilitate collaboration across various stakeholders, including patients, caregivers, clinicians, and administrative staff, to enhance the efficiency, safety, and quality of healthcare delivery[7].
Dynamic automation approaches further augment the benefits of these frameworks by enabling more adaptable and maintainable automation solutions. By dividing the execution process into functional reusable capabilities that can be dynamically orchestrated, dynamic automation allows for easier maintenance and faster adaptation to changing requirements[11]. This method not only reduces development and testing efforts by approximately 40% but also ensures that updates can be seamlessly integrated without significant disruptions to existing workflows[11].
Automation Development Lifecycle
The automation development lifecycle in the healthcare industry involves several critical phases aimed at understanding and addressing specific business problems through automated solutions. These phases include requirement gathering, solution modeling, identification of test scenarios, development of the automation solution in the appropriate technology, testing, and deployment[6].
Requirement Gathering and Solution Modeling
The first step in the automation development life cycle is understanding the current business problem and building a solution model to address it[6]. This involves detailed analysis and mapping of existing workflows, considering the roles, needs, and responsibilities of multiple stakeholders involved[10]. Effective requirement gathering is crucial as it lays the foundation for the entire automation process.
Identification of Test Scenarios
Once the requirements are gathered and a solution model is built, the next step is identifying test scenarios. This phase is essential to ensure that the automation solution will function correctly and efficiently in the intended environment[6]. Evaluating the likelihood and impact of potential risks to the system, such as incomplete or misleading data and procedural failures, is a part of this phase[9][12].
Development
The development phase involves creating the automation solution based on the identified requirements and test scenarios. This phase often requires a robust technical infrastructure capable of supporting the desired automation activities[6]. Due to the frequently changing requirements and timeline constraints in healthcare, even simple business problems might require updates and retesting of several code components[6].
Testing and Deployment
Testing is a critical phase where the developed automation solution is rigorously tested to ensure it meets the required standards and functions as expected. This phase helps identify and rectify any issues before the solution is deployed in a real-time environment[6]. Following successful testing, the automation solution is deployed, marking the final phase of the lifecycle.
Challenges and Dynamic Automation
One of the main challenges in the automation development lifecycle is managing the frequently changing requirements and the need for constant updates and retesting[6]. This makes the implementation of automation solutions difficult and time-consuming. Dynamic automation can address these issues by dividing the execution process into multiple functional reusable capabilities, which can be maintained and tested with ease. This approach improves productivity and reduces the time required for development and testing[6].
Dynamic Automation
Dynamic automation is a sophisticated approach aimed at enhancing productivity and efficiency in healthcare by allowing the execution of code components to be customized through configurations via solution modeling. This approach contrasts with traditional static automation, where any small update necessitates significant changes and investment due to the rigid nature of the workflow. In dynamic automation, the entire execution process flow is divided into multiple functional reusable capabilities that can be dynamically called during the execution flow as required, thus ensuring flexibility and ease of maintenance[6].
Components of Dynamic Automation
Leader
The Leader acts as the master code that orchestrates the entire execution process. It initiates the automation, manages the execution queue, and commands other components to perform their respective tasks. This central control ensures that the automation flow remains organized and efficient, even when dealing with complex and dynamic requirements[6][7].
Dispatcher
The Dispatcher serves as a monitoring system that detects any changes in the design model and updates the backend call algorithm accordingly. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that the execution process adapts to new requirements and data inputs dynamically. The Dispatcher works closely with the requirements modeling tool to extract and load updated scripts into a staging repository[6].
Executor
The Executor is responsible for executing the reusable capability modules based on the instructions from the Dispatcher. It retrieves the necessary scripts from the repository and runs the corresponding code components. Upon completion, the Executor stores the results in a results repository and reports back to the Leader, ensuring a seamless execution flow[6].
Framework Prerequisites
The framework for dynamic automation necessitates several prerequisites:
- A master table listing all reusable capability modules and the required input parameters.
- A repository containing the algorithm code for the Leader, Dispatcher, and Executors.
- A requirements modeling tool that dynamically generates scripts in a shared staging repository for requirement updates[6].
Execution Process
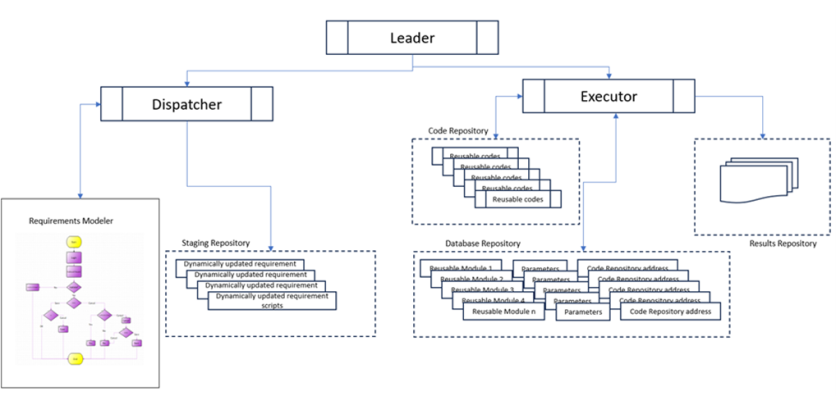
The execution process of dynamic automation in the healthcare industry involves several meticulously coordinated steps to ensure efficient and reliable automation of workflows[6][7].
- Initiation by Leader: The Leader commands the Dispatcher to begin the automation execution. It also checks if any execution thread is already in progress and manages the queue order.
- Requirement Extraction: The Dispatcher executes the requirements modeling tool, extracts updated requirement scripts, loads them into the staging repository, and notifies the Leader upon completion.
- Execution Command: The Leader commands the Executor to execute the automation based on the updated scripts in the staging repository.
- Execution by Executor: The Executor retrieves the scripts, executes the reusable code from the repository, stores the results, and confirms the completion to the Leader.
This approach divides the execution flow into multiple functional reusable capabilities, which can be dynamically invoked as required, leading to easier maintenance and testing.
Benefits
Dynamic automation offers multiple benefits[6]:
- Ease of Maintenance and Testing: Small chunks of automation code are easier to maintain and test.
- Adaptability to Changes: The execution is driven by requirements, ensuring that any new changes are accounted for during the execution process flow.
- Reusability: Reusable codes can be utilized across various automation flow processes, reducing redundant development and maintenance work.
- Development and Testing Efficiency: It saves approximately 40% of development and testing effort, thus reducing the time to market.
- Multithreaded Execution: The Leader facilitates multithreaded automation execution, enhancing overall efficiency.
Example: Prescription Fulfillment Process
In the context of a pharmacy, dynamic automation can significantly streamline the prescription fulfillment process.
- Patient profile creation
- Prescription request creation
- Validation of drug interaction with patient medications, prior authorization steps, days supply rule validations, and other drug-related validations
- Prescriber validation
- Health insurance validation and claims processing
- Prescription fulfillment
Given the thousands of rules and complex scenarios involved in each step, a dynamic automation approach ensures that updates are seamlessly integrated without disrupting the entire workflow, thus providing a robust and flexible solution[5].
The Impact of Dynamic Automation
Dynamic automation offers several key advantages that make it a valuable approach in the healthcare industry. One of the primary benefits is the ease of maintenance and testing. Because the automation code is divided into small, reusable components, it can be more readily maintained and tested, reducing the overall complexity of the system. This modular approach ensures that updates or changes to specific parts of the workflow do not necessitate extensive rework of the entire automation process, thereby saving significant time and resources[6][7].
Another significant benefit of dynamic automation is its adaptability to changing requirements. Since the execution is driven by up-to-date requirements, any new changes are automatically accounted for during the execution process flow. This ensures that the automation system remains current with evolving healthcare practices and regulatory requirements, thereby improving its efficacy and reliability[9][10].
The reusability of code components in dynamic automation also reduces redundant development and maintenance work. By utilizing the same reusable modules across different automation workflows, organizations can streamline their processes and minimize the duplication of effort, leading to more efficient operations[6][11].
Dynamic automation also results in considerable savings in development and testing efforts. Studies indicate that this approach can save approximately 40% of development and testing effort, thereby accelerating the time to market for new automation solutions. This is particularly crucial in the healthcare industry, where timely implementation of automation can lead to improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency[6][8].
Additionally, the multi-threaded execution capability facilitated by the Leader component in dynamic automation enables simultaneous execution of multiple tasks. This not only enhances the overall throughput of the system but also ensures that healthcare providers can deliver timely and effective care to patients[9][12].
Conclusion
Due to the increased demand for access to care for better health outcomes and improved productivity, automation is inevitable in the healthcare industry. A dynamic automation approach will help build automation faster and more dynamically, which in turn will help serve customers and their patients in better health.
References
[1] Peterson, T. (2020, November 4). 12 Reasons Why Automated Care Is Helpful in the Healthcare Industry. Advanced Data Systems Corporation. https://www.adsc.com/blog/reasons-why-automated-care-helpful-in-healthcare-industry
[2] Butterfield, S. (2024). Automation In Hospitals And Healthcare. Divbyte. https://divbyte.com/automation-in-hospitals-and-healthcare/
[3] Office Practicum. (2024). 6 Common Challenges in EHR Implementation. Office Practicum. https://www.officepracticum.com/blog/6-common-challenges-in-ehr-implementation
[4] Wikipedia contributors. (2020, October). Electronic health record. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_health_record
[5] Bajwa, J., Munir, A. U., Nori, A., & Williams, B. (2021). Artificial intelligence in healthcare: transforming the practice of medicine. Future Healthcare Journal, 8(2), e188–e194. https://doi.org/10.7861/fhj.2021-0095
[6] Zayas-Cabán, T., Haque, S. N., & Kemper, N. (2021). Identifying Opportunities for Workflow Automation in Health Care: Lessons Learned from Other Industries. Applied Clinical Informatics, 12(3), 686–697. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1731744
[7] Zayas-Cabán, T., Okubo, T. H., & Posnack, S. (2023). Priorities to accelerate workflow automation in health care. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 30(1), 195–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocac197
[8] Sutton, R. T., Pincock, D., Baumgart, D. C., Sadowski, D. C., Fedorak, R. N., & Kroeker, K. I. (2020). An overview of clinical decision support systems: benefits, risks, and strategies for success. NPJ Digital Medicine, 3, 17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-020-0221-y
[9] Aguirre, R. R., Suarez, O., Fuentes, M., & Sanchez-Gonzalez, M. A. (2019). Electronic Health Record Implementation: A Review of Resources and Tools. Cureus, 11(9), e5649. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.5649
[10] Impact. (2023, May 17). 10 Benefits of Process Automation. Impact. https://www.impactmybiz.com/blog/advantages-of-process-automation/
[11] Kanade, V. (2024, February 26). What Is Automation? Definition, Types, Benefits, and Importance. Spiceworks. https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/artificial-intelligence/articles/what-is-automation/
[12] Office for Civil Rights (OCR). (2022, October 19). Summary of the HIPAA Security Rule. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/security/laws-regulations/index.html
About the Author
Sivasakthivel Ramamoorthy is the Director of Client Services Automation at CVS Health, a Fortune 6 company. Sivasakthivel is a target-oriented solutionist, innovator, automation architect, business leader, adaptive learner, and out-of-the-box thinker. He played an instrumental role in modernizing healthcare pharmaceuticals and plan benefit management automation.
ⓒ 2025 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




