As artificial intelligence (AI) revolutionizes industries worldwide, from personalized marketing to advanced data analytics, concerns about data privacy are also on the rise. Centralized AI platforms have become the primary collectors of vast amounts of personal data, leading to deepening privacy concerns among users.
A survey found that 70% of respondents have little or no trust in companies to make responsible decisions regarding AI use. Furthermore, nearly 80% of respondents believe that personal information collected through AI will be used in ways not originally intended.

Centralized platforms, such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon, dominate data collection, creating data silos that limit interoperability and reduce users' control over their personal information. The concentration of data in the hands of a few companies increases the risks of data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized data exploitation.
How Centralized AI Exploits User Data
Current AI models are designed to learn and improve from vast datasets, often collected secretly or through misleading terms and conditions. AI-powered ad platforms analyze user behavior to create detailed profiles that are then sold to advertisers. While this technology can result in more relevant ads, it also means that users' digital footprints are being monetized without their permission.
However, the benefits of AI-driven personalization come with significant trade-offs, as the underlying practices raise serious concerns about the accuracy, legality, and security of the data being used.
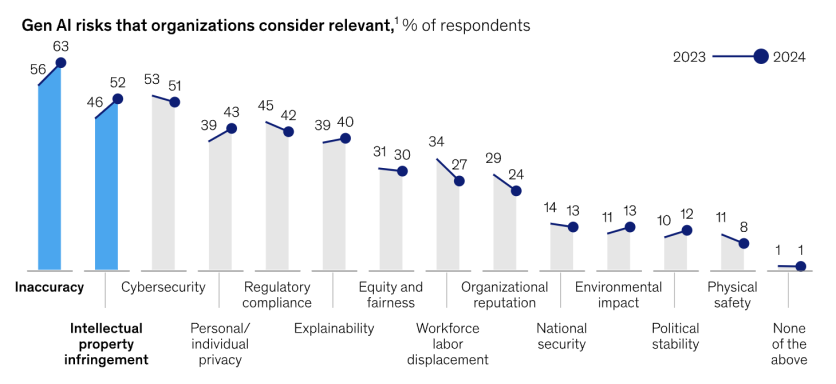
Studies show that inaccuracies, intellectual property infringements, and cybersecurity breaches are common issues associated with AI use. As businesses become increasingly aware of these risks, they recognize the vital connection between data privacy and customer trust. Many believe that customers will stop doing business with them if they fail to protect their data adequately.
Securing Digital Identity with Decentralized Identifiers
As the internet evolves, Web3 is emerging as a more user-centric, decentralized ecosystem. Unlike Web 2.0, where data is controlled by centralized entities, Web3 leverages blockchain technology to give users ownership of their digital identities and assets. Despite its potential, Web3 still faces challenges, particularly in managing data securely across multiple platforms.
By offering a transformative approach to managing digital identities, this is where Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) come into play. Unlike traditional models tied to specific platforms, DIDs are decentralized and can be used across a variety of services without compromising user privacy. This technology is actively used by the decentralized AI blockchain Matchain through its data aggregator MatchID, which ensures that data is only shared with explicit consent and for intended purposes.
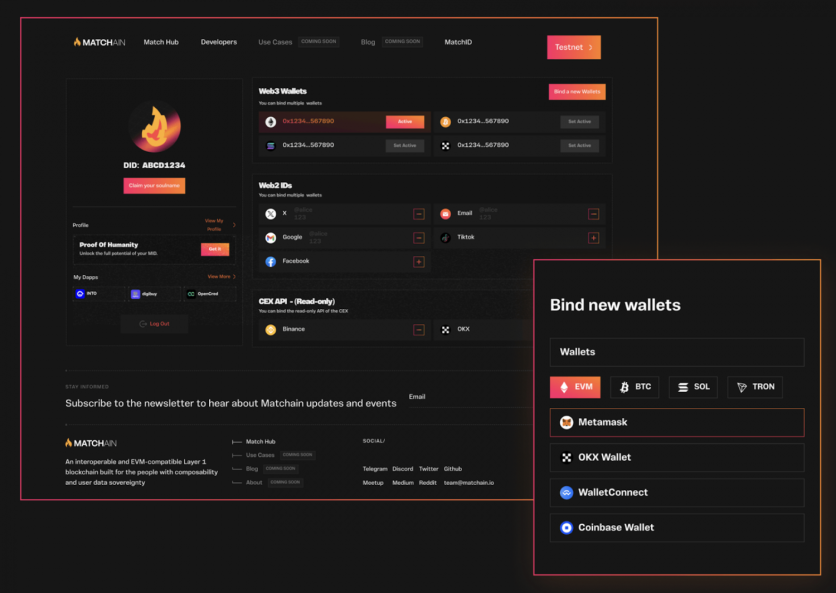
MatchID redefines digital identity with a low-threshold DID registry that seamlessly integrates Web2 users and bridges interactions across multiple blockchains. It also provides users with a dashboard displaying their data score or value based on their digital footprint and activities across various apps and decentralized applications (dApps).
Additionally, Matchain officially launched its mainnet after the construction, optimization and BNB Chain migration process. The platform, which reached more than 180 million transactions during the testnet process, has established more than 50 ecosystems and strategic partnerships, including Dapps, wallets and exchanges.
Advantages of Decentralized Data Management
Decentralized data management offers numerous benefits over traditional centralized systems. First and foremost, it empowers users to regain control over their data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and misuse. In a decentralized model, data is distributed across multiple nodes, making it more resilient to cybersecurity threats.
Moreover, decentralized systems promote interoperability, allowing seamless data exchange across different platforms and apps.
Ethical AI Practices: Setting New Standards
As AI continues to evolve, the need for ethical practices becomes increasingly critical. Matchain seeks to set new standards in this area, focusing on transparency, user consent, and data sovereignty. By integrating decentralized technologies into its AI-driven platform, Matchain ensures that users' privacy is protected and that their data is used ethically. The platform's approach aligns with Web3's core principles and addresses the growing demand for more responsible AI practices.

In summary, while the dominance of centralized AI platforms has raised significant concerns about user privacy and data security, the rise of Web3 technologies like decentralized identifiers stands as a promising solution. By giving users control over their digital identities and data, decentralized systems like Matchain are paving the way for a more secure and privacy-focused internet.
As developers continue to adopt decentralized solutions, a future where AI and digital identity align with privacy, security, and user sovereignty principles is within reach.
ⓒ 2025 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




