Advancements in neuroscience and robotics have been separate, but this world's first study from Chinese researchers has now been delivered on a robot controlled by human brain cells alone. No, it is not connected to a living person via a brain chip, as it uses the actual grey matter, and is among the earliest breakthroughs in biocomputation.
This development is unique, as it does not need a living person to control it via wireless or wired connections from the brain; only the human organ is needed for the bot's processes.
World's First Human Brain-Controlled Robot Arrives from China
According to a release from China's Tianjin University (via Xinhua News Agency), a scientific research team has successfully developed a new brain-computer interface with an intelligent interaction system called MetaBOC. This was made possible through the collaboration of the Haihe Laboratory team from Tianjin University and Southern University of Science and Technology.
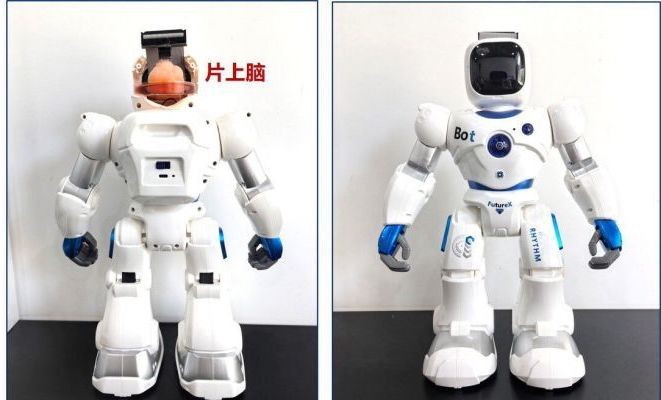
It is also regarded as an "on-chip brain," which consists of an electrode chip and a real human in-vitro brain, making it possible for it to function as a "brain-on-a-chip" device.
Instead of using the human brain alone, this fuses it with the chip to deliver a brain-computer interface (BCI), which is meant to deliver "hybrid intelligence."
No Need for Humans, Only Their Brains for This Bot
The study did not need to involve humans and implant them with chips to control the robot, as the organ was used to create this new kind of hybrid intelligence for the machine.
The human biological brain created "brain-like tissue" through stem cell culture technology to live outside the body and then uses the chip for scientists to deliver its functions, debug it, and teach the brain knowledge for autonomous bot control.
Neuroscience and Robotics Developments
The two separate fields of science, Neuroscience and Robotics, have been going their own way as both are still complex studies in today's age, but some have looked into fusing both together for more advanced developments. Among the most popular neuroscience-focused companies is Elon Musk's Neuralink, best known for its success in its first human test, with the patient calling it an 'aimbot' for gaming.
On the other hand, robotics has seen massive developments over the years, and it centers on different focuses, including autonomous helpers or factory workers, offering limbs for amputees, and more. However, some developments focused on making robots more human-like, with one study looking to advance humanoid robots with emotion recognition.
While both fields are not exactly exclusive to each study, there have been little developments in fusing both into one technological advancement, with this new research proving that it is possible and has already happened. Tianjin University's recent study successfully used human brain cells to power a robot, calling it 'brain on a chip,' paving the way for the future of biocomputation worldwide.
Related Article: MIT Develops Prosthetic Legs Controlled by Amputees' Nervous System

ⓒ 2026 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




