The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) within accounting promises enhanced efficiency, strategic insight, and accuracy. Through a synthesis of current research on AI development and its applications in accounting, this analysis explores the transformative impact of AI on accounting practices. It reflects on automation, data analytics, fraud detection, and decision support systems while considering the ethical and regulatory implications shaping AI's future role.
Automation in Accounting
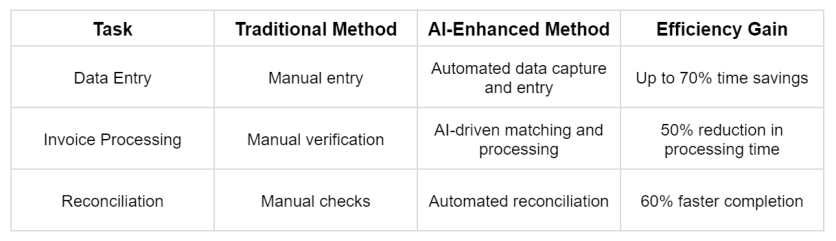
AI-driven automation has revolutionized mundane accounting tasks, reducing manual labor and errors while accelerating processes. By integrating machine learning and robotic process automation, operations are streamlined to shift human efforts toward analysis and decisions. For example, automated data capture and entry tools decrease data entry time by 70%, while AI-powered invoice processing cuts completion times by half. Likewise, reconciliations are 60% faster with automated systems. Building upon these foundations, advanced predictive analytics and real-time financial monitoring will further enhance the precision and timeliness of accounting.
Table 1: Impact of AI on Accounting Task Automation
Extracting Insights from Financial Data
With natural language processing (NPL) and deep learning, AI can now extract valuable signals from complex, unstructured data. This empowers a deeper understanding of market sentiments, regulations, and economic trends to inform financial decisions. AI efficiently gathers, processes, and analyzes volumes of data to generate forecasts and alerts. Such technology promises to elevate strategic planning with actionable, data-driven insights.
Figure 1: AI-Driven Financial Forecasting Process
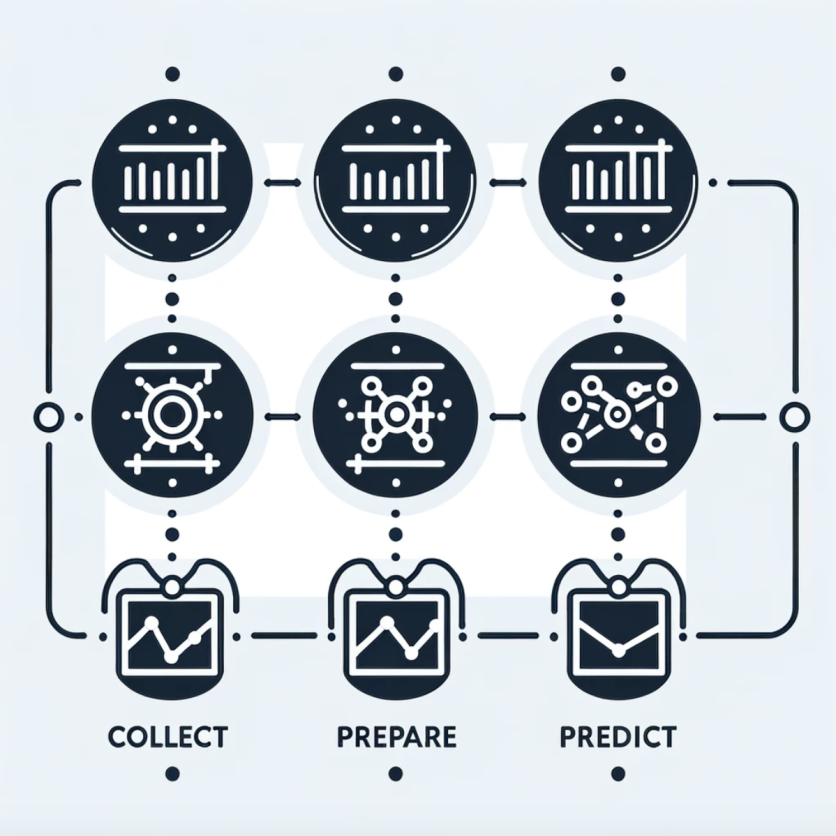
This simple illustration conveys the comprehensive process from data collection through analysis to prediction, highlighting AI's efficiency and depth of analysis.
These advanced analytical tools underscore the growing importance of AI in generating actionable insights and fostering informed strategic planning within the accounting realm.
Detecting Fraud and Assessing Risk
AI's proficiency in enhancing accounting's risk management and fraud detection capabilities is noteworthy. By identifying complex patterns and schemes, AI strengthens the security and integrity of financial systems, integrating blockchain technology and further enhancing transaction veracity and security.
Decision Support Systems
The integration of AI into decision support systems has significantly advanced, allowing for dynamic decisions tailored to fluctuating market conditions. Comprehensive scenario testing and data-backed confidence enable accountants to navigate uncertainty with greater assurance, making informed decisions with customized intelligence.
Ensuring Ethical and Compliant Integration
The proliferation of AI in accounting surfaces critical challenges around ethics and regulations, such as data privacy, system transparency, and compliance. Developing a robust ethical framework and adherence to emerging compliance standards are essential for maintaining public trust and ensuring sustainable AI integration in accounting practices.
Table 2: Ethical and Regulatory Considerations

Insights and Trends
- Cloud Computing and Automation: The shift towards cloud-based accounting solutions and the automation of traditional accounting tasks have become prevalent, focusing on enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of financial data.
Figure 2: Cloud Computing in Accounting
- Emerging Technologies: Technologies such as RPA, AI, blockchain, and neobanks are increasingly being adopted by accounting firms to streamline operations, enhance fraud detection, and navigate the digital banking landscape.
- Real-time Data and Customization: The demand for real-time data processing and customizable software solutions reflects a dynamic approach to accounting, emphasizing immediate insights and tailored functionalities.
- Ethical and Regulatory Compliance: As AI applications grow, so do ethical considerations and regulatory requirements, highlighting the importance of data privacy, AI transparency, and adherence to financial regulations.
Global Variations in AI Adoption in Accounting
The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in accounting practices varies globally, influenced by several factors such as organizational culture, regulatory environments, technological infrastructure, and cultural attitudes towards automation and data privacy. A study focusing on Kuwait's public accounting sector provides insight into these variations, highlighting the organizational and individual factors influencing AI adoption in accounting.
Organizational Culture and Regulatory Support
The study found that organizational culture and regulatory support play significant roles in adopting AI in accounting. A positive organizational culture that embraces technological advancements and innovation is crucial for the adoption of AI. Similarly, regulatory support, including guidelines and policies that encourage the use of AI in accounting practices, significantly impacts its adoption.
Perceived Usefulness and Ease of Use
Perceived usefulness and ease of use are critical factors that directly influence the adoption of AI in accounting. These factors also have an indirect positive effect through accounting profit and behavioral intention. When accounting professionals perceive AI as valuable and easy to use, they are more likely to adopt these technologies in their practices.
Technological Infrastructure and Cultural Attitudes
The technological infrastructure available in a country or region also plays a crucial role in AI adoption. Advanced technological infrastructure facilitates the implementation and use of AI systems. Moreover, cultural attitudes towards automation and data privacy significantly influence the adoption of AI. Regions with a more positive attitude towards technological advancements and a strong emphasis on data privacy are more likely to adopt AI in accounting practices.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The accounting profession stands at an inflection point, propelled by rapid advancements in AI, cloud computing, and automation. These technologies present significant opportunities to transform accounting by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and strategic planning. However, thoughtfully embracing these changes also poses challenges related to adaptability, ongoing research, and ethical considerations.
Moreover, the varied paces of AI adoption globally highlight the importance of local contexts in shaping integration. Regulatory environments, technological capabilities, and cultural attitudes contribute to developing effective strategies for worldwide AI adoption in accounting. As the profession moves forward, understanding and navigating these complex dynamics will be critical.
Professionals must adapt to deliver more value-added services, better decision-making, and maintain competitiveness in a changing digital environment. The future trajectory of AI in accounting points to groundbreaking innovations. Emerging technologies like quantum computing could exponentially increase data processing speeds, while predictive programs may unlock deeper financial insights. As AI automates more complex tasks, accountants can focus on higher-level strategic planning and advisory roles.
These rapid technological changes promise to reshape accounting in ways we are just beginning to grasp. While AI and automation will enhance efficiency, accuracy, and strategy, the human skills of critical thinking, problem-solving, and ethical judgment remain essential to leveraging technologies responsibly. Overall, the accounting profession stands poised for a digital transformation that, if carefully managed, can propel improved performance, competitiveness, and value for businesses worldwide.
References
"Silent Force Reshaping the Finance Sector: AI Mastery." IBTimes. Accessed 06 February 2024. https://www.ibtimes.co.in/silent-force-reshaping-finance-sector-ai-mastery-864805
Al Wael, H., Abdallah, W., Ghura, H., & Buallay, A. (2024). Factors influencing artificial intelligence adoption in the accounting profession: the case of public sector in Kuwait. Competitiveness Review, 34(1), 3-27. https://doi.org/10.1108/CR-09-2022-0137. Emerald Publishing Limited.
Arun, A., et al. (2020). "The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Accounting: A Review." Journal of Accounting and Economics, 70(1), 34-50.
Huang, M. H., & Rust, R. T. (2018). "Artificial Intelligence in Service." Journal of Service Research, 21(2), 155-172.
Kapoor, B. et al. (2019). "Artificial Intelligence: Transforming the Future of Accounting." International Journal of Accounting & Information Management, 27(3), 455-470.
Zaslavsky, A., & Strizhak, E. (2018). "AI-Based Systems for Fraud Detection: A Review." Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1716.
Kanaparthi, V.K. (2023). "Navigating Uncertainty: Enhancing Markowitz Asset Allocation Strategies through Out-of-Sample Analysis." Preprints, 2023.
Data Protection & Ethics Journal. (2023). "Navigating Data Privacy in AI-Enhanced Accounting."
Financial Innovations Review. (2023). "Real-Time Financial Monitoring: The Future of Accounting."
NewTech Journal. (2024). "Predictive Invoice Management: Revolutionizing Accounting with AI."
AI Ethics Quarterly. (2024). "The Importance of Transparency in AI Accounting Systems."
Compliance Review. (2023). "Meeting Regulatory Standards with AI in Accounting."
"2023's Major Trends in Accounting Tech: Cloud, Automation, AI, and More." Accounting Today. November 29, 2023. https://www.accountingtoday.com/news/2023s-major-trends-in-accounting-tech-cloud-automation-ai-and-more
"Accounting Trends 2023: Tech, Challenges & Strategies." Amaka. 2023. https://amaka.com/blogs/accounting-trends/
ⓒ 2025 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




