Offering a unique perspective on this famous constellation, NASA unveils an image that features the hidden allure of the Orion.
While Orion is readily recognizable in the night sky, NASA's Picture of the Day unveils a more detailed and intricate view of the constellation, made possible through a digital camera lens and sophisticated post-processing techniques.
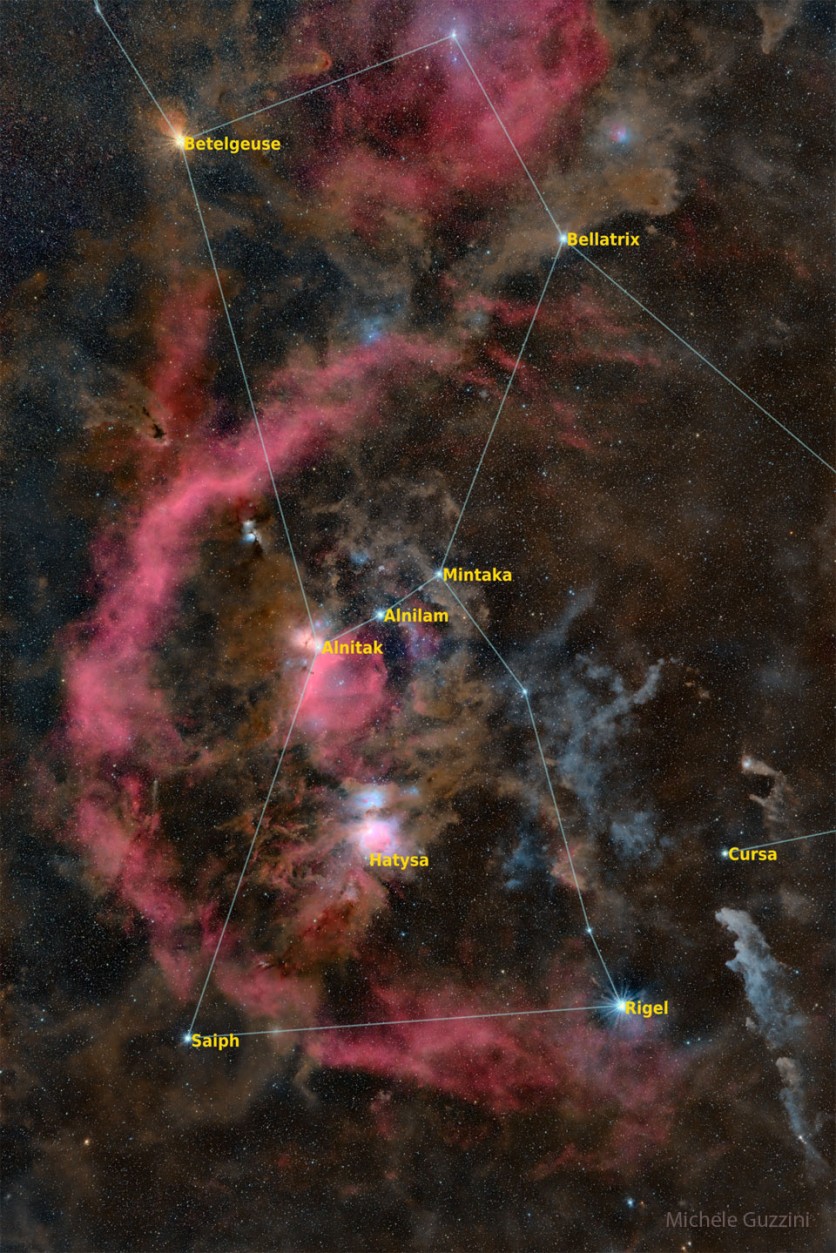
NASA's Picture of the Day Features the Orion
The mesmerizing image showcases the prominent red giant Betelgeuse, which appears on a vibrant orange tint. Betelgeuse stands out as the brightest star on the constellation's upper left.
On the lower right, Orion's hot blue stars, including the supergiant Rigel, create a dazzling display. The upper right features Bellatrix, another one of Orion's blue stars, contributing to the constellation's celestial beauty.
Aligned in Orion's belt are three stars situated approximately 1,500 light-years away, originating from the constellation's extensively studied interstellar clouds.
Just below Orion's belt, a bright and somewhat fuzzy patch known as Orion's Nebula comes into view. Though faint to the naked eye, this stellar nursery becomes strikingly visible in this long-exposure image.
An intriguing feature captured in the image is Barnard's Loop, a massive gaseous emission nebula enveloping Orion's Belt and Nebula. Discovered over a century ago by the pioneering Orion photographer E. E. Barnard, this loop adds a captivating element to the overall composition.
Orion, known for its distinct shape and prominent stars, becomes a celestial masterpiece in this long-exposure image, revealing details and nuances not easily observed with the naked eye. The interplay of colors, from the cool reds to the hot blues, creates a visually stunning representation of this well-known constellation.
Read Also : NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Snaps Wide-Angle View of the Orion Nebula in Dreamy Aura
Orion's Prominent Stars
NASA noted that the Orion constellation has two prominent stars: Betelgeuse and Rigel. Betelgeuse, a red supergiant on Orion's right shoulder, is relatively youthful at approximately 10 million years old in stellar terms.
Its significant size and accelerated life cycle make it a fascinating celestial object, especially compared to our nearly 5-billion-year-old Sun.
While there is a sense of anticipation regarding the possibility of Betelgeuse undergoing a supernova explosion, current observations suggest that such an event is not imminent, according to NASA.
On the other hand, Rigel, the blue supergiant positioned on Orion's left foot, is also a young star with an estimated age of 8 million years. Despite being farther from Earth than Betelgeuse, Rigel's inherent brightness distinguishes it as the brightest star in Orion and one of the most prominent in the night sky.
The long exposure image not only captures the celestial beauty of Orion but also provides a glimpse into the fascinating lives of these stellar members, each contributing to the captivating narrative written across the cosmic canvas.
Related Article : NASA's Hubble Space Telescope Captures 'Orion Nebula's Dreamy Cloudscape' With Over 500 Exposures!

ⓒ 2025 TECHTIMES.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.




